Fraud prevention tips
Fraud prevention starts with understanding the risks and taking proactive steps to safeguard your personal data and financial accounts. By increasing your fraud awareness and staying alert to common scam prevention tactics, you can reduce the chances of becoming a victim. Here are some common ways to protect your identity and assets.
Password security
Use strong, unique passwords and enable security features on all your devices, keeping software and apps regularly updated to support effective fraud prevention.
Email vigilance
Be cautious with emails and links. Never provide personal information via email and verify suspicious messages carefully to enhance fraud detection and scam prevention.
Safe connectivity
Avoid using public Wi-Fi for financial transactions; if necessary, use a VPN and always sign out from shared devices to maintain strong fraud prevention practices.
Mail protection
Protect your mail by shredding sensitive documents, opting for paperless statements, and securing your mailbox, especially when away, as part of your overall fraud awareness strategy.
Social privacy
Limit personal information shared on social media and review privacy settings to reduce identity theft risks and improve fraud awareness
Phone safety
Never share personal or financial info during unsolicited phone calls and always verify the caller’s identity before providing any details to aid in scam prevention and fraud detection.
Identifying suspicious email
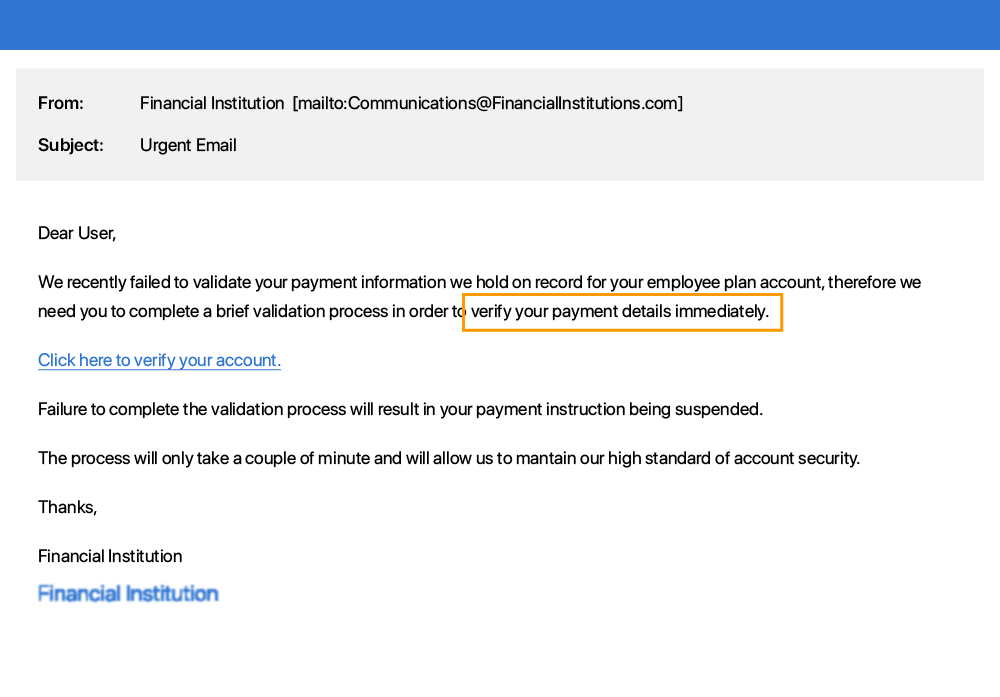
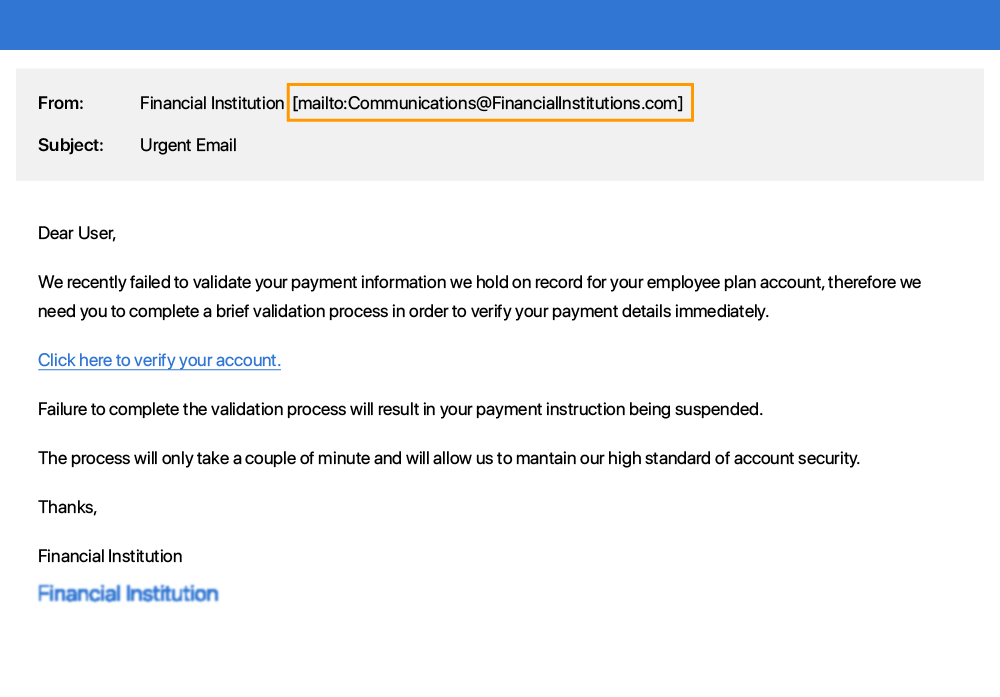
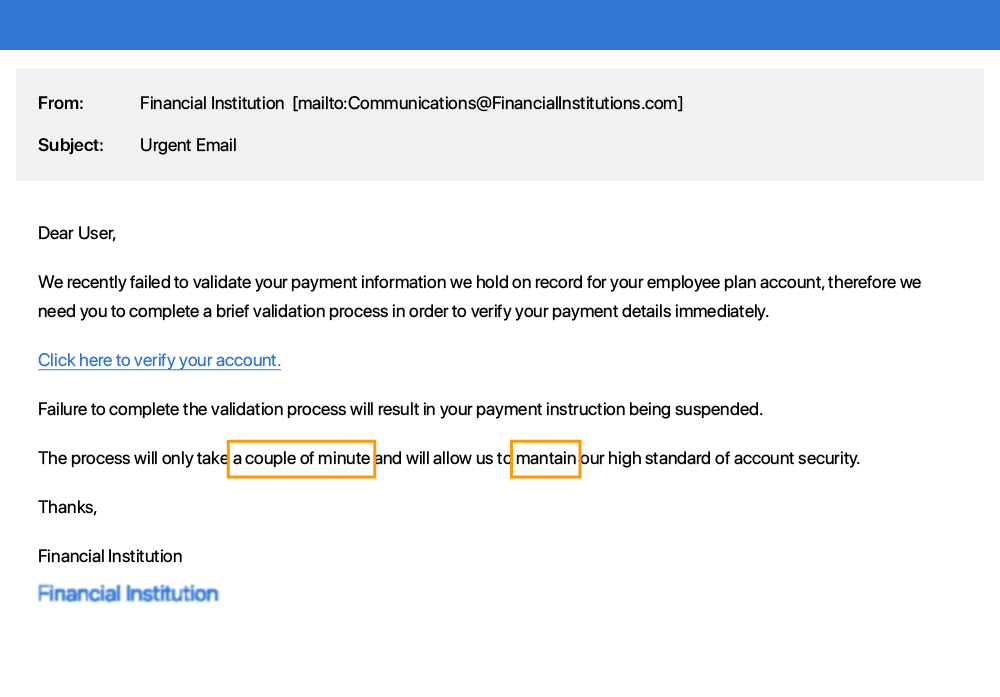
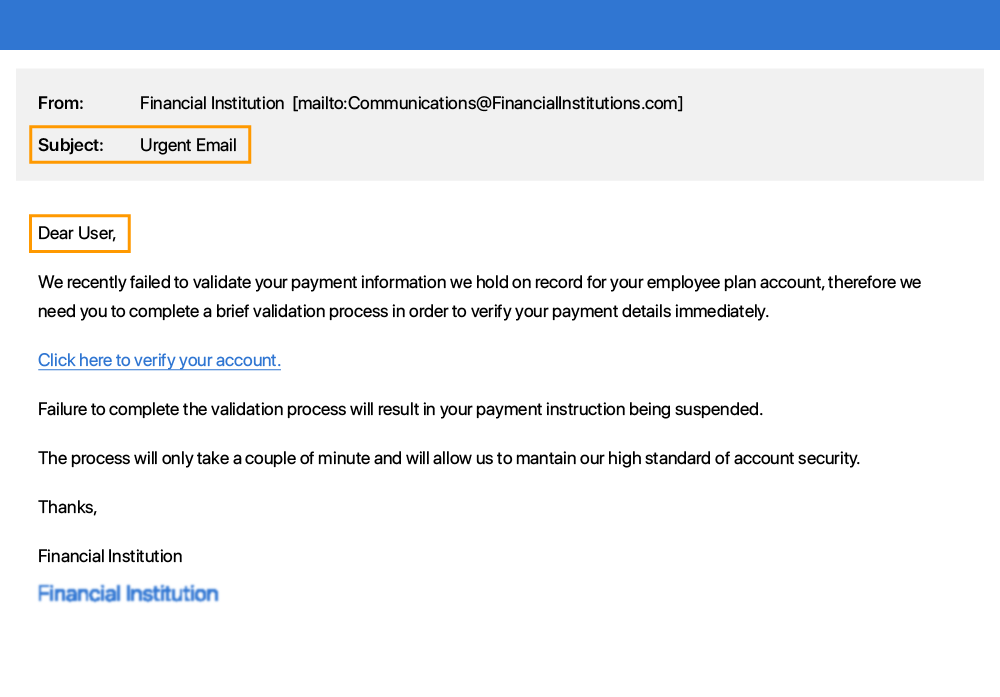
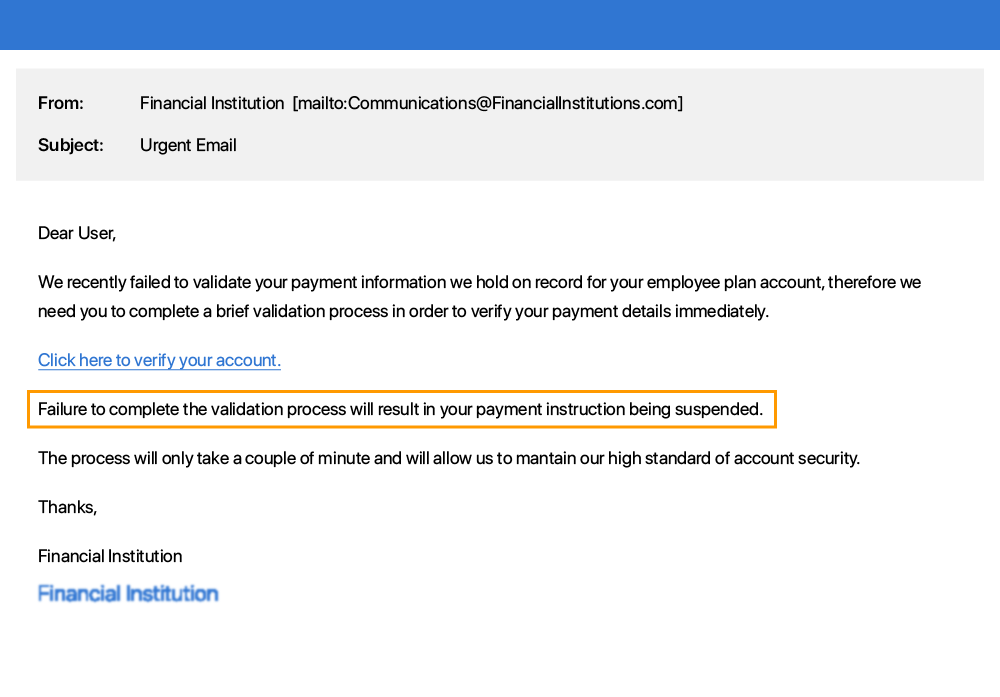
Immediate action required or a sense of urgency communicated e.g. your account will be deleted if you do not respond to this email.
Glossary
Here are some common terms people use when talking about fraud and identify theft.
Identity theft, also known as identity fraud, is a crime in which an imposter obtains key pieces of personally identifiable information, such as Social Security or driver's license numbers, in order to impersonate someone else.
A keylogger or keystroke logger is a type of software that tracks or logs the keys struck on your keyboard, typically in a covert manner so that you don’t know that your actions are being monitored.
Software that is intended to damage or disable computers and computer systems.
A type of malicious software designed to block access to a computer system until a sum of money is paid.
The use of deception to manipulate someone into giving away confidential or personal information that may be used for fraud.
Spying on the user of an ATM, computer, or other electronic device in order to obtain their personal access information.
Spyware is software that enables a user to obtain covert information about another's computer activities by transmitting data.
making phone calls or leaving voice messages supposedly from reputable companies in order to get people to reveal their personal information, such as bank details and credit card numbers.
A VPN creates a virtual encrypted tunnel between you and a remote server operated by a VPN service. All external internet traffic is routed through this tunnel, so your data is secure from prying eyes. Use of a VPN computer also gives you the appearance of having an IP address of the VPN server, masking your identity.
The content on this page is provided for informational purposes and is not intended to provide authoritative information security, data protection, or other professional or legal advice. Links to third party web sites and content do not constitute an endorsement or sponsorship by Computershare and Computershare does not represent or warrant that the contents of those web sites are accurate, compliant with state or federal law, or compliant with copyright or other intellectual property laws. Any reliance on the contents of a third-party web site is at your own risk, and you assume all responsibilities and consequences resulting from such reliance.