Phishing is the fraudulent practice of sending emails purporting to be from reputable companies in order to get individuals to reveal personal information, such as passwords and credit card numbers.
Phishing is the fraudulent practice of sending emails purporting to be from reputable companies in order to get individuals to reveal personal information, such as passwords and credit card numbers.- To prevent phishing you have to be able to recognise it. Emails attempting to get your personal information are a giveaway, but you should be cautious about receiving unexpected emails from friends as well.
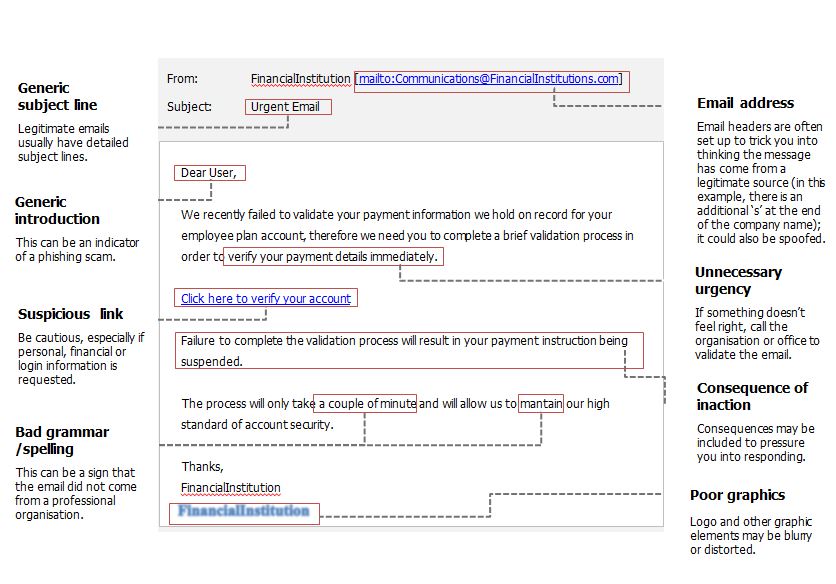
- Signs of a suspicious email:
- Poor grammar or spelling mistakes.
- The email is addressed to a group of users, a shared mailbox or to a distribution list rather than being addressed to you directly.
- Immediate action required or a sense of urgency communicated e.g. your account will be deleted if you do not respond to this email.
- Fuzzy or blurry images.
- Sender's email address does not match the company it purports to come from.
- Computershare email addresses will generally match our websites, for example @computershare.com, or will match with an additional country code, such as @computershare.co.uk.
- Some Computershare emails may come from @e-computershare.co.uk.
- If you receive an email that looks suspicious, DELETE it without clicking on the links or opening attachments.
- Be cautious about opening any attachments or downloading files from emails regardless of who is sending them – if it is a link to a website, you should hover the mouse over the link in the email and look carefully at the web address to make sure it is genuine – including that the company name is spelled correctly. Type web addresses into your browser rather than clicking on links.
- Be aware that links and attachments can also carry spyware, so even if you are not asked for personal information this can be obtained via a Keystroke Logger which can record the keys you press when typing.
- Remember the email may look legitimate, but legitimate businesses and financial institutions will never ask for personal information via an email.
- Although phishing is generally used when talking about email, phishing attacks are also common on social media sites - Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn and many more.
Here is an example of what a phishing email could look like: